As technology continues to advance, our reliance on internet connectivity has become more prevalent than ever. From businesses to personal use, the need for a stable and high-speed internet connection is crucial. This is where Wide Area Networks (WANs) come into play. They are the backbone of modern communication, providing an efficient way of connecting geographically dispersed locations. In this article, we will dive deep into the world of WANs, exploring its functionalities, benefits, and everything in between.
What is a Wide Area Network?
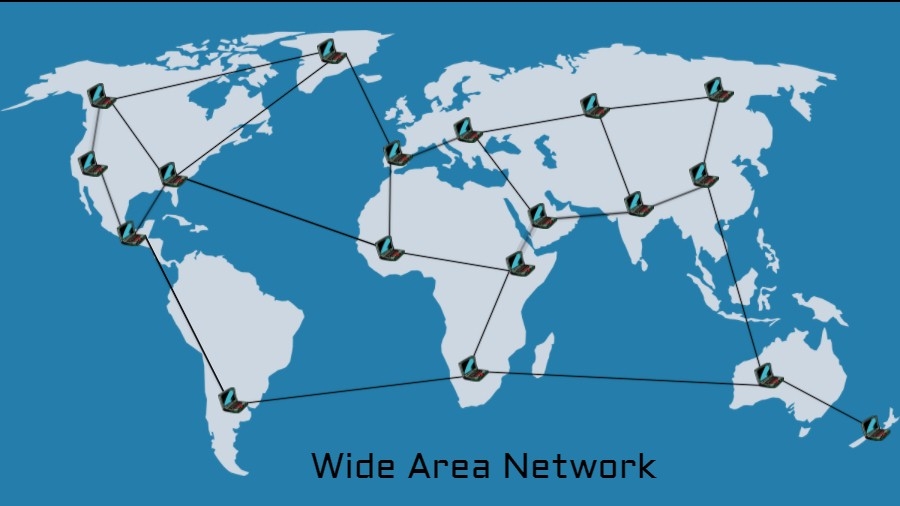
A Wide Area Network, as the name suggests, is a type of computer network that covers a large geographical area, connecting multiple smaller networks together. It serves as a bridge between different Local Area Networks (LANs) spread across various cities, states, or even countries. For instance, a company with offices in different countries can use a WAN to connect all their branches, enabling seamless communication and data sharing between them.
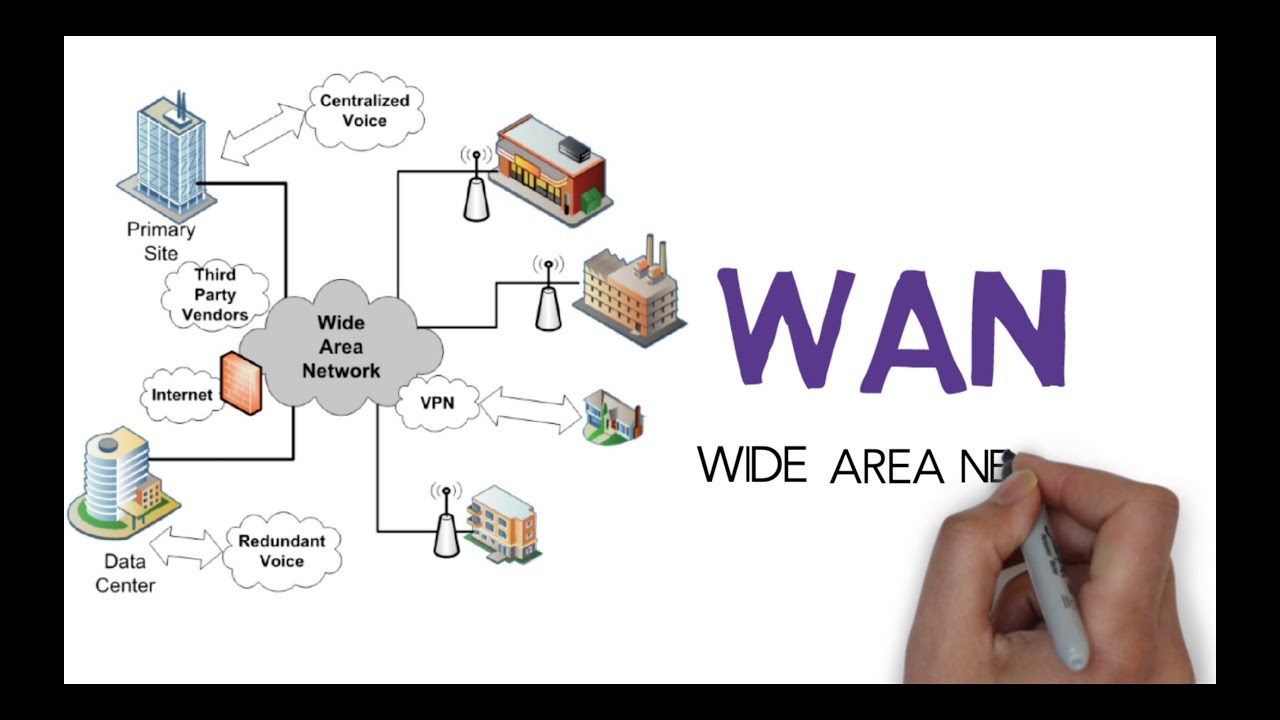
A Wide Area Network (WAN) is a computer network that spans a large geographic area, linking several smaller networks together
The Evolution of Wide Area Networks
The concept of WANs dates back to the late 1960s when the Advanced Research Projects Agency Network (ARPANET) was developed to connect computers at research institutions and universities. Over time, as the internet evolved, so did WANs. With the development of new technologies, such as fiber optics, satellite links, and microwave transmission, WANs became faster, more reliable, and cost-effective.
Today, most companies use either a leased-line or a Virtual Private Network (VPN) to create their WAN infrastructure. Leased-lines use public telecommunication lines to connect LANs, while VPNs use the internet as a medium for data transmission. Both methods offer similar functionalities, but VPNs are more preferred due to their cost-effectiveness.
Components of a Wide Area Network
To understand how WANs function, it is essential to know its components. These include:
- Routers: Routers are the backbone of any WAN infrastructure. They are responsible for routing data packets between different networks, ensuring they reach their intended destination.
- Switches: Just like routers, switches play a vital role in ensuring data packets are transmitted efficiently within the WAN. They direct data to specific devices on a network and can also segment traffic to improve network performance.
- Modems: A modem is responsible for converting digital signals into analog signals that can be transmitted over telephone lines. In a WAN setup, they are used to connect remote offices to the central network.
- Multiplexers: Multiplexers, also known as muxes, allow multiple data streams to be transmitted simultaneously over a single communication channel. They are used to optimize bandwidth usage and reduce costs.
- Firewalls: Firewalls are essential in securing a WAN from external threats. They monitor incoming and outgoing traffic, blocking any unauthorized access to the network.
Types of Wide Area Networks
There are several types of WANs, each with its unique features and functionalities. Some of the most common ones include:
Circuit-switched WANs
Circuit-switched WANs use a dedicated connection between two points. When a call or data transfer is initiated, the circuit is set up, and the connection remains active until the session is terminated. This type of WAN is commonly used for phone calls, video conferencing, and internet connections via dial-up modems.
Packet-switched WANs
Packet-switched WANs use divided data packets to transmit information between networks. These packets travel through various nodes before they reach their destination, where they are reassembled into their original form. This type of WAN offers a more efficient way of data transmission compared to circuit-switched WANs.
Cell-switched WANs
Cell-switched WANs use a combination of both circuit-switching and packet-switching techniques. The data is divided into small fixed-sized cells, which are then transmitted over a circuit-switched connection. This method is commonly used for voice and video transmission, as it offers better quality and reliability.
Ethernet WANs
Ethernet WANs use Ethernet technology to connect devices over a wide area network. It is primarily used in local and metropolitan networks but can also be extended to cover larger geographical areas. This type of WAN offers high-speed data transfer and scalability, making it a popular choice among businesses.
Advantages of Wide Area Networks
The implementation of a WAN infrastructure comes with several benefits for both businesses and individuals. Some of these advantages include:
- Cost-effective: By connecting multiple LANs together, companies can save on costs that would have been incurred by setting up individual networks for each branch.
- Improved communication: WANs allow employees in different locations to communicate seamlessly via video conferencing, instant messaging, or voice calls. This improves collaboration and productivity within the organization.
- Centralized management: With a WAN, all network resources and services can be centrally managed from one location. This makes it easier to monitor and troubleshoot any network issues that may arise.
- Global connectivity: WANs enable organizations to establish connections with remote offices, partners, suppliers, and customers across the globe. This promotes global expansion and enhances business relationships.
- Secure data sharing: With built-in security features such as firewalls and encryption, WANs provide a secure platform for data sharing between different branches of an organization.
Challenges of Wide Area Networks
While WANs offer numerous benefits, they also come with their fair share of challenges. Some of the most common ones include:
- High initial setup cost: The initial cost of setting up a WAN infrastructure can be quite high, especially for small businesses. This includes purchasing networking equipment, leasing lines, and hiring IT professionals to manage the network.
- Security risks: As WANs cover a larger geographical area, they are more susceptible to security threats compared to LANs. Companies have to invest in robust security measures to protect their network from external attacks.
- Reliability concerns: If the main connection or server goes down, all the connected branches will also lose connectivity. This can lead to downtime and loss of productivity for businesses.
- Maintenance costs: Maintaining a WAN infrastructure requires continuous monitoring and regular updates to ensure optimal performance. This can result in additional costs for companies, especially if they have a large number of branches or remote offices.
How to Set up a Wide Area Network?
Setting up a WAN can be a daunting task, especially for those without technical expertise. However, with proper planning and the right tools and equipment, it can be done successfully. Below are the steps involved in setting up a WAN infrastructure:
Establishing a WAN can be challenging, particularly for individuals lacking technical expertise
Identify your needs
The first step towards setting up a WAN is to identify your business needs. Do you need global connectivity? Will you be using real-time applications such as video conferencing? Understanding your requirements will help you determine the type of WAN that best suits your organization.
Choose a WAN technology
Once you have identified your needs, you can then select the type of WAN that meets those requirements. Consider factors such as cost, speed, scalability, and reliability when making your choice.
Select a service provider
After selecting the appropriate WAN technology, the next step is to choose a service provider. Look for a reputable provider with a track record of offering reliable services and good customer support.
Create a network diagram
Before setting up the physical infrastructure, it is essential to create a detailed network diagram. This will help you visualize how the network will be set up, allowing you to make any necessary changes before implementation.
Install networking equipment
Install the necessary networking equipment, including routers, switches, and firewalls, according to the network diagram. It is essential to follow best practices when setting up the equipment to ensure optimal performance.
6. Configure the network
Once the hardware is in place, the next step is to configure the network settings. This includes assigning IP addresses, setting up security measures, and defining network policies.
7. Test the network
After configuring the network, it is crucial to test it to ensure everything is working correctly. Conduct speed tests, check for connectivity between branches, and verify that all security measures are functioning as intended.
Future of Wide Area Networks
With the ever-growing demand for a reliable and high-speed internet connection, the future of WANs looks promising. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see more efficient and cost-effective WAN solutions in the market. Some of the trends that are likely to shape the future of WANs include:

Given the increasing need for dependable and fast internet connections, the outlook for WANs appears optimistic
- Software-Defined WANs (SD-WANs): SD-WANs use software-defined networking (SDN) technology to manage and secure wide area networks. They offer better scalability and flexibility compared to traditional WANs, making them an attractive option for businesses.
- Cloud-based WANs: Cloud-based WANs leverage the power of cloud computing to provide a more affordable and scalable solution for connecting remote offices. With the rise of cloud-based services, we can expect to see more companies adopting this approach to their WAN infrastructure.
- 5G technology: The introduction of 5G technology will revolutionize the way WANs operate. With faster speeds and lower latency, 5G will enable real-time applications such as video conferencing and remote desktop access to function seamlessly over a wide area network.
- Internet of Things (IoT): As more devices become connected to the internet, the need for a robust WAN infrastructure will increase. IoT devices will require a stable and high-speed connection to transmit data, making WANs an essential component of this technology.
- Edge computing: Edge computing is the practice of processing data closer to the source, reducing the need for data to travel long distances over a WAN. This approach will result in faster data transfer speeds and improved network performance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Wide Area Networks play a vital role in connecting the world today. They have enabled businesses to expand their reach, improve communication, and increase productivity. With the continuous advancement of technology, we can expect to see more efficient and cost-effective WAN solutions in the future. As organizations continue to rely on the internet for their day-to-day operations, the importance of WANs cannot be overstated. It is safe to say that they are here to stay and will continue to shape the way we communicate and share information in the years to come.
